Flame Spread Index For Class A Roof

Smoke developed index 0 450 fire class a designation refers to material that may ignite but will not sustain a flame.
Flame spread index for class a roof. On very low slope commercial structures even a glaze coating of pure asphalt may meet class a flame spread. To achieve a class a rating the roof must be effective against severe fire exposure. The flame spread categories are as follows per astm e 84 ul 723. And class iii or c with a 76 200 fsr.
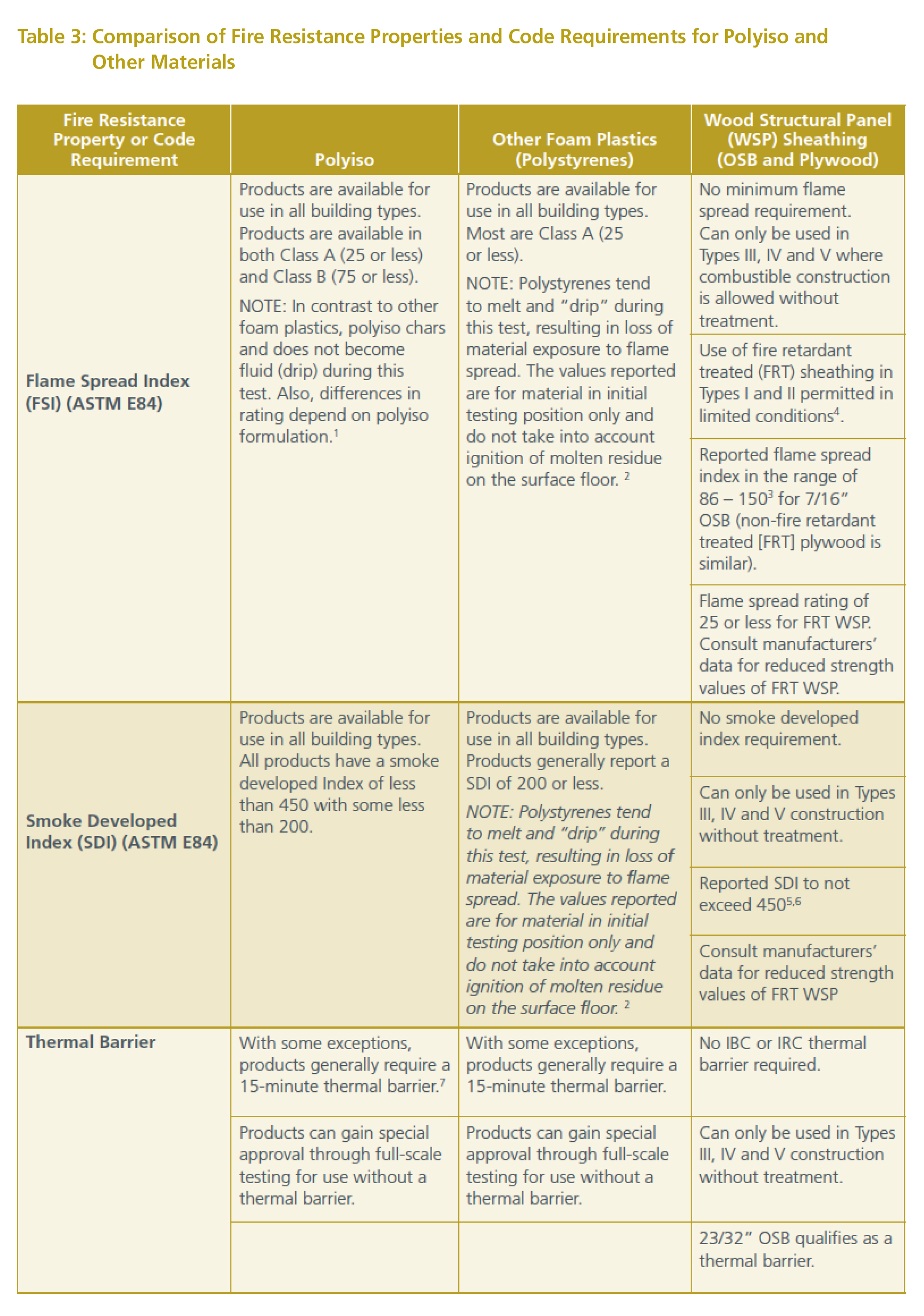
The most commonly used flame spread classifications are. An fm class 1 designation means the roof assembly has been subjected to a series of tests in addition to external and internal fire exposure including wind uplift water leakage and impact resistance. Polyiso remains the only foam plastic insulation product for direct application to steel roof decks to earn fm approval for class 1 roof systems. The maximum flame spread is 6 feet for a class a rated roof 8 feet for class b and 13 feet for class c.
Fsi is the measurement for the speed at which flames progress across the interior surface of a building while sdi measures the amount of smoke a sample emits as it burns. Gravel surfaced built up roofing and ballasted single ply systems usually meet class a while mineral surfaced roofings may be class b. Flame spread and smoke development astm e84 in order to obtain the flame spread classification results must fall into a range between 0 and 25 to be class a 26 75 for class b and 76 200 for class c. Foam plastic used for insulating interior walls ceilings and floors of commercial buildings requires class i foam having a flame spread index of 75 or less in some circumstances 25 or less and smoke developed index of 450 or less.
Fibrated coatings and asphalt emulsions retain the class a to higher slopes as do the fr modified and fr single ply systems. Through the e 84 test both the flame spread index fsi and smoke developed index sdi are reported for a given sample. Experience maximum flame spread of 6 feet. Flame spread index 76 200.
Flame spread 26 to 75 other fr surface coatings class c or iii. Class a products will not generate excessive visibility obscuring smoke an important factor in designing safe egress for building occupants. The slope of the test specimen is preselected and since steeper slopes are more of a challenge due to melting material feeding the fire the rating applies to the maximum slope passed. Class a or i.
The scale is divided into three classes. In general inorganic materials such as brick or tile are class i materials. This is proven if it can. Class ii or b with a 26 75 fsr.
In all cases smoke development must be less than 450. Class i or a with a 0 25 fsr. Flame spread 25 or less frtw some fr surface coatings class b or ii. Whole wood materials are usually class ii while reconstituted wood materials such as plywood particle board or hardboard are class iii.
When conducting healthcare renovations almost all facilities require temporary containment materials to be used the meet the astm e 84 class a fire rated requirement. Class a roofing is the preferred choice for any home but this type of roofing is particularly important if you live in an area that is prone to wildfires.